When Lori Robertson’s cancer returned, doctors noted she might only have a year left to live. But a clinical trial made her options look brighter.
5:00 AM
Author |
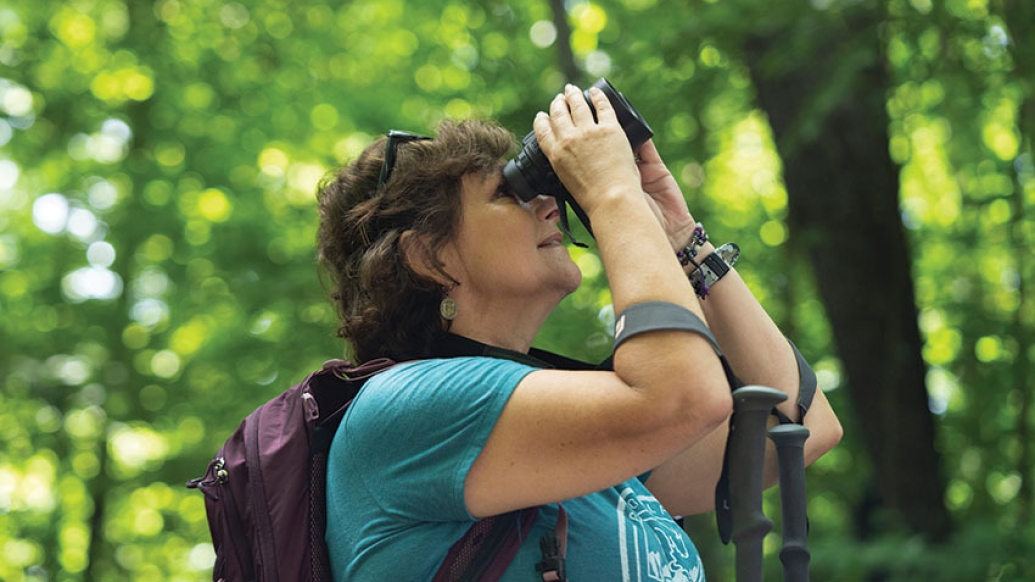

When Lori Robertson met with Rogel Cancer Center medical oncologist Vaibhav Sahai, M.B.B.S., M.S., to talk about cancer treatment options, she remembers little of what he said.
Lori had just found out her rare bile duct cancer had not only returned several years after undergoing surgery but had also spread to the lining of her abdomen. She and her family had recently gone hiking in Denali National Park and Preserve, and even with the strenuous exercise, she'd felt fantastic. So she was shocked to hear that she had cancer again.
"You know the old adage when you get your cancer diagnosis and you go to the doctor and they talk to you and you cannot hear what they're saying?" Lori said. "That's true. You look at the doctor and nod your head yes, but you can't really hear or retain anything."
What she did recall: She had the option to enroll in a phase 1 clinical trial, an early-stage research study that investigates the ideal dose for a potential new drug. Although the results for this trial were still preliminary and more testing needed to be done to say whether the treatment was effective, early signs had been promising for people with Lori's type of cancer.
"There's one open spot left," said Sahai, who leads this multi-site trial. "It's yours if you want it."
Lori signed up for the trial that day.
"The prognosis was not too good, and when you're in that situation, you're willing to try anything," Lori said. "The trial gave us that glimmer of hope, that optimism that maybe we would come out of this on the other side."
On trial
Lori started coming into the cancer center for her trial treatment the week after she enrolled in the study.
Her first task was to get her bloodwork done with pathology, a group she says was as crucial to her positive experience with the cancer center as Sahai.
"I can't stress how important the lab people are," Lori said. "The day starts with them. They can make or break your whole day."
SEE ALSO: HIPEC Treatment Targets Tough Cancers by 'Bathing' Tumors in Chemo
Then she headed to the Ravitz Cancer Center Research Unit, a tucked-away room on the second floor that serves as the infusion area for early-phase Rogel clinical trials.

There, Lori received two chemotherapies in combination with devimistat, an intravenous drug that blocks cancer cells from producing the energy the cells need to survive. (In phase 1 trials, every patient receives the study drug.)
"In theory, if you switch off their energy source, cancer cells should die," said Sahai, who leads the section of gastrointestinal medical oncology at Michigan Medicine and is a nationally recognized expert in bile duct cancer. "But that's not always the case."
The days at Ravitz were long — 12 hours at times. But, on Mondays, Lori's nurse was often Jessica Pott, R.N. The two both had children who attended Western Michigan University, and that personal connection helped Lori feel calmer.
"I would give her the plan for the day but then tried to draw her out a bit personally," Pott said. "I think she then felt more comfortable opening up and telling me what she was scared of."
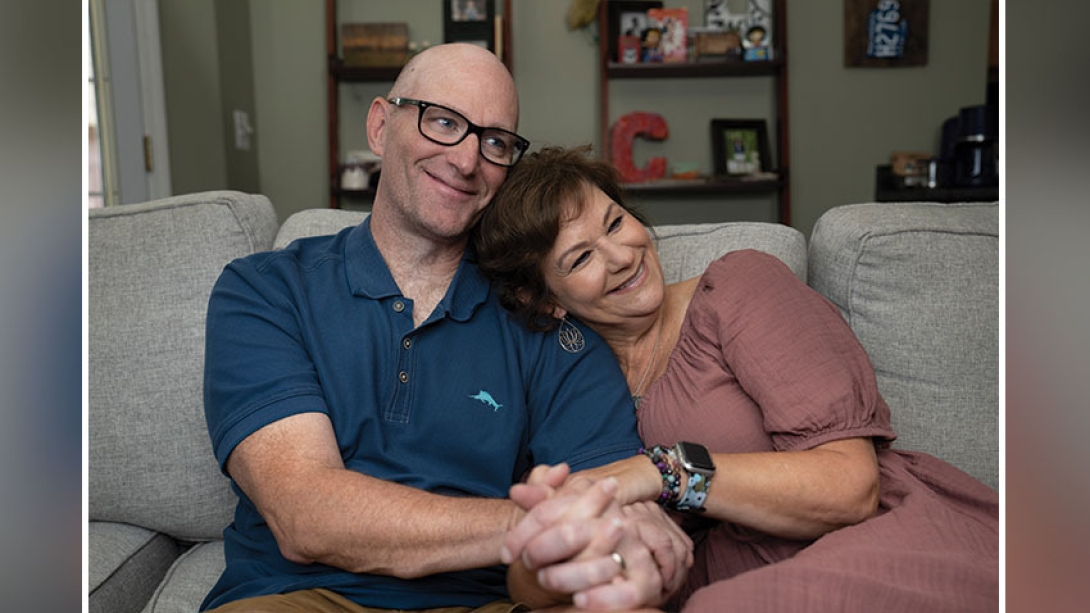
Lori had indeed fallen into despair. It was difficult for her to believe she might only have a year left to live. At one point, her anxiety levels were so high that she needed her husband, Robb, to be in contact with her when she sat on the couch, her leg on his, his hand resting on her arm.
"It was a tough year," Lori said. "Jess and Robb really pulled me through a lot of those bad days."
Her neighbors had a plan to help, too. Around Berkley, the community outside of Detroit where Lori lives, signs began appearing with a teal heart and her initials.

The signs were the brainchild of Diane Haroutunian-Brus, a friend of Lori's, who'd wanted to give Lori a boost and been amazed at the number of people who felt the same way.
"I still have people in my phone with the initials 'LR' next to them to remind me why I know them," Haroutunian-Brus said.
The neighborhood wasn't done yet. At 9 p.m. on Lori's birthday in mid-August, Robb suggested going for a walk. The couple walk frequently, so Lori wasn't expecting anything unusual — until she saw a group gathered at the end of her driveway and luminarias all the way down the street.
Lori started crying.
"I was sobbing and sobbing and sobbing," Lori said. "I think that was the release I needed."
A positive response to a clinical trial
Luckily, fate seemed to have more positive things in store for Lori. By November, her tumor had shrunk significantly. On her January scans, it was no longer visible. There was now a possibility that the cancer could be surgically removed.
"Oftentimes, we'll have patients that do really well on clinical trials we're running and will need a surgeon as part of their care," said Filip Bednar, M.D., Ph.D., a surgical oncologist who co-leads the peritoneal malignancy program at Michigan Medicine with Donnele Daley, M.D., "even though originally they were not a good candidate for an operation."
Lori was even eligible for heated intraperitoneal chemotherapy, or HIPEC, a form of chemo that is pumped into the abdomen during surgery to treat cancer that has spread to the abdominal lining.
Like Podcasts? Add the Michigan Medicine News Break on Spotify, Apple Podcasts or anywhere you listen to podcasts.
HIPEC isn't typically a treatment option for patients with bile duct cancer because this type of cancer tends to come back in multiple regions of the abdomen or in other organs, like the lungs or liver.
SEE ALSO: 6 Key Facts About Clinical Trials (uofmhealth.org)
"The patients that benefit the most from HIPEC have relatively low amounts of tumor in the abdomen," Bednar said. "Lori had such a good response, and she'd survived for so long with all of her other treatments that it was pretty reasonable for us to try to completely clear her disease."
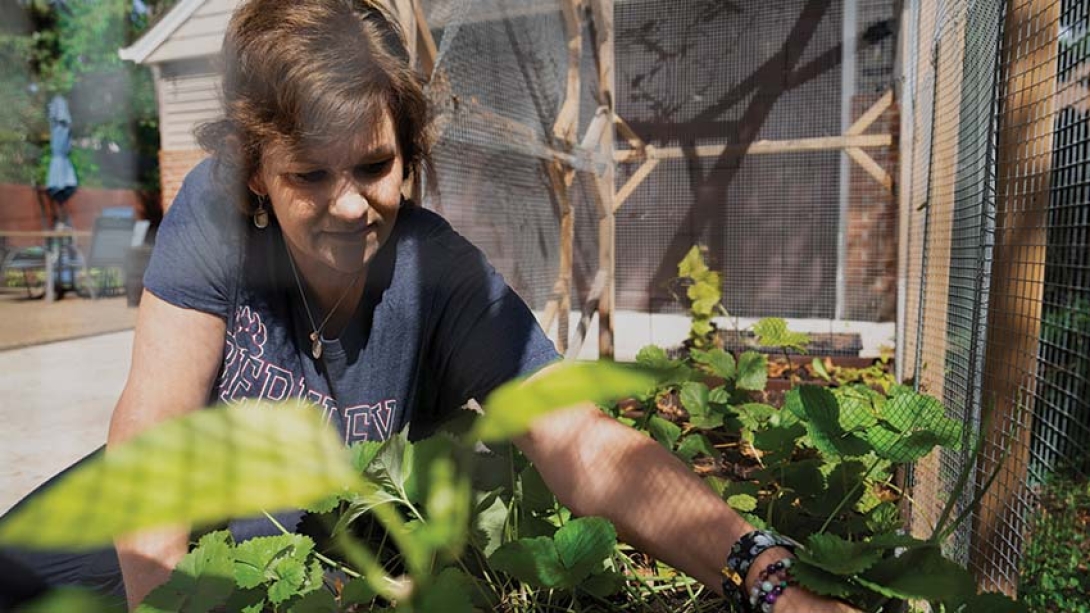

When Lori underwent surgery, Bednar found microscopic bits of cancer, but otherwise, the rest of the tumor had died — even before he administered HIPEC.
"Lori's type of tumor is typically very challenging to treat," Sahai said. "It's unique to see such a high degree of response. Her story highlights the need for us to identify the exceptional scenarios and what makes these patients so responsive to this particular therapy."
"The same doctor who told us that Lori might have a year left to live looked at her scans and said they couldn't find any cancer," Robb said. "That's remarkable."
Using her experience to help others
In August, Lori's first scans since her surgery came back clean. She says she expects round three of her cancer to come eventually but hopes that day won't be for many years.
She's been open about her experience, sharing on her personal Facebook page and in support groups. A man who Googled the study drug she was taking even found one of her posts and reached out. He ended up enrolling in the next phase of the same study and was randomized to the arm of the trial that didn't include the devimistat.
"I share because 1) it helps me to get it off my chest but 2) it could help somebody else," Lori said. "I'm constantly telling people to get a second opinion, to look into Dr. Sahai, to look into Michigan Medicine. That slogan, 'the leaders and best' — that's true."
Live your healthiest life: Get tips from top experts weekly. Subscribe to the Michigan Health blog newsletter
Headlines from the frontlines: The power of scientific discovery harnessed and delivered to your inbox every week. Subscribe to the Michigan Health Lab blog newsletter

Explore a variety of healthcare news & stories by visiting the Health Lab home page for more articles.

Department of Communication at Michigan Medicine
Want top health & research news weekly? Sign up for Health Lab’s newsletters today!