A pediatrician provides valuable information on homemade formula, milk alternatives and other resources during national shortage.
2:20 PM
Author |
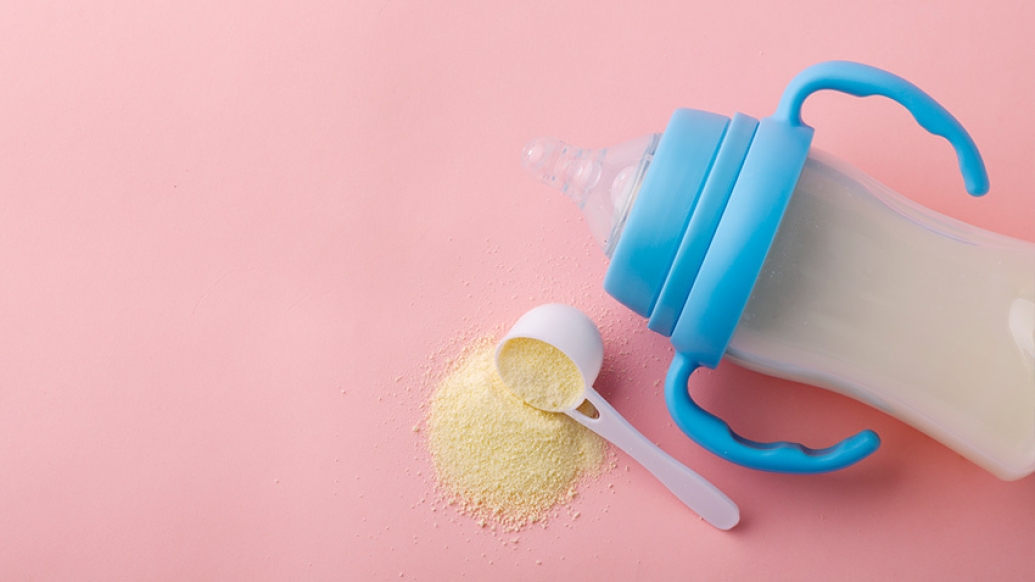

The nation's stock of baby formula is shrinking—and the messaging around the subject can be overwhelming.
What can parents who rely on formula do during this time?
"We're trying to provide reassurance that there are alternative options to help babies get the nourishment they need," said LaDonna Hendricks-Sparrow, M.D., a pediatrician at University of Michigan Health C.S. Mott Children's Hospital. "Our top goal while navigating this situation is to ensure babies are safe."
Hendricks-Sparrow offers five pieces of advice for parents and guardians worried about feeding their babies during the national shortage.
1. For babies over 6 months, cow's milk is OK for the short term
Cow's milk previously wasn't recommended for children younger than one. But amid the formula shortage, the American Academy of Pediatrics has said babies six months and older can have whole cow's milk as long as they don't need specialty formula for allergies or other health needs.
Hendricks-Sparrow notes that this is a temporary solution for children under 12 months old. The biggest concern with cow's milk is the risk of anemia because it doesn't have enough nutrients. That's why she recommends supplementing milk with iron-rich foods such as fortified infant cereals or pureed beans, spinach and meats.
Parents should also avoid plant-based milk (almond, oat, etc.), she notes, because they aren't fortified with the necessary iron, protein and vitamins needed to nourish babies.
For babies with allergies or who need specialized formula, she recommends store brands, which haven't been as affected by the shortage and often have hypoallergic options.
2. Homemade or diluted formula can be dangerous
Hendricks-Sparrow warns against homemade formulas, which are not recommended by the AAP.
"The formula making process is complicated enough, making sure it includes proper nutrition like enough protein, fats, minerals, electrolytes and sodium. This is not something we want people to try to do in their own kitchens," she said.
Hospitals and doctors across the country have also seen babies hospitalized due to altered formulas, both from dilution and homemade versions that cause infections, severe dehydration, vitamin deficiencies and anemia. It can also lead to seizures.
"People can forget just how much is happening within the first 12 months of a baby's life," Hendricks-Sparrow said. "Their brains and bodies are growing, and proper nutrition is crucial."
3. Vet sources carefully when seeking alternative formula sources
While some online suppliers, such as Amazon, may have legitimate options, Hendricks-Sparrow says, parents should be mindful of fraud and formula auction sites that may sell unsafe products that are not FDA approved. Some may even use a logo that looks like a well-known brand.
She also encourages her patients to check in with smaller local grocery stores who may not be affected by the shortage. There may be local social media groups you can join to connect with parents who have extra formula—just be sure to check the expiration dates and recalled products.
You can also look to properly vetted milk banks who screen for safe breastmilk instead of buying milk directly from a mother. Breastmilk that is not properly vetted through a milk bank can be unsafe for babies as you may not know what type of medications or infections babies may be exposed to through donated breastmilk from individuals.
"We want to make sure babies get nourished without seeking unsafe alternatives that may lead to longer term consequences with growth and development down the road," Hendricks-Sparrow said.
Although your local hospital or doctor's office may have formula on supply, these are small sample amounts for emergency situations, Hendricks-Sparrow explained: "They have enough to help families with a couple of feeds while they're there, but not enough to meet these shortage needs."
She also stresses that parents only buy up to two weeks' worth of formula during the shortage so that other families can have access to the supply. This is an AAP recommendation as well.
4. Watch for signs of poor developmental growth
Hendricks-Sparrow explains that signs of malnutrition in babies may be seen early on as "fussy" or "inconsolable". Later, the baby may be more lethargic, not producing enough wet diapers, not producing tears (dehydration) and have seizures.
"If you notice any of these signs, you should immediately seek medical attention," she said.
5. Talk to your child's health provider
The first thing Hendricks-Sparrow wants concerned parents to do is reach out to their pediatrician for support.
"I am okay with my patients Googling and using that to spark a conversation with me. We're here as a resource, and we can help connect you with community resources such as social workers in our department and even churches who have a food bank," she said.
Parents may be feeling isolated as they are processing the input from a variety of sources both close to home and from afar. Hendricks-Sparrow recognizes that isolation can be dangerous if a patient is listening to information online and through family and friends without consulting their pediatrician.
"We spend time with each family individually to discuss what's best for their specific child," she said.

Explore a variety of healthcare news & stories by visiting the Health Lab home page for more articles.

Department of Communication at Michigan Medicine
Want top health & research news weekly? Sign up for Health Lab’s newsletters today!