Planning to take your kids sledding this winter? Get need-to-know guidelines from one family who has seen the safety risks firsthand.
10:00 AM
Author |

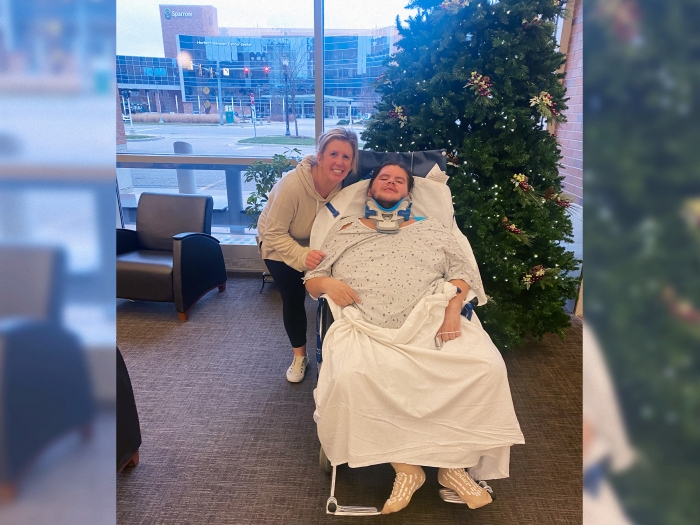
It was a blustery January day, just one week before her 10th birthday. Bailey Knight hopped on a sled with her older cousin to glide down a sledding hill enjoyed by children for more than two decades.
But what started as a fun snow day with family and friends near Kalamazoo, Michigan, turned into a night in the emergency room for the then fourth grader after the pair's sled slammed full speed into a wooden light pole. Bailey was ultimately transferred to the Michigan Medicine C.S. Mott Children's Hospital with a crushed nose, fractured cheek bones, bilateral eye orbit fractures, a skull fracture and tears in the lining of her brain.
Her injuries were severe, requiring a nearly 19-hour surgery by Mott teams within three days of the accident.
Today, the 19-year-old is attending beauty school at J. Douglas Aveda in Grand Rapids, inspired by her experience with the annual Glamour Day organized by the Mott Craniofacial Anomalies program.

But her family knows her outcome could have been different. Bailey's mom, Kimberly Graves, now cautions other parents to take extra, often skipped, steps before sledding with their kids: thoroughly investigate surroundings, use helmets and look out vigilantly for hazards such as poles and trees.
"We were just trying to have a fun day. People have been going sledding for years. We did it as kids. We weren't thinking of it as something dangerous," Graves says of the 2011 accident. "I even went with Bailey the first time we sledded that day. Families had been sledding on that same exact hill for over 25 years.
MORE FROM MICHIGAN: Sign up for our weekly newsletter
"We never imagined anything like this ever happening. It's so hard to get that image of your child out of your head."
More than 20,000 emergency department visits a year are related to sledding incidents among children under age 19 in the United States, research suggests.
Peter Ehrlich, M.D., director of the Mott Pediatric Trauma Center, says head injuries and broken bones are among the most common injuries from sledding incidents.
Data evaluated by Ehrlich and colleagues in 2014 showed that by 2010, sledding injuries constituted the leading cause of hospitalization at Mott for all winter activities. Of the 52 children who were hospitalized from sledding injuries over an eight-year period, 37% of patients suffered a head injury and the majority of them were admitted to the intensive care unit. Three children had permanent disability including cognitive impairment, and two others required long term hospitalization rehabilitation.
Several emergency cases also involved sleds being towed by motorized vehicles such as snowmobiles or four-wheelers.
Ehrlich said experts in injury prevention are promoting head protection for sledding just as they advise helmet use for downhill skiing and biking.
"People often think of sledding as a mostly safe winter activity with a low risk of injury. However, a significant number of traumatic brain injuries are related to sledding," Ehrlich says.
LISTEN UP: Add the Michigan Medicine News Break to your Alexa-enabled device, or subscribe to our daily updates on iTunes, Google Play and Stitcher.
"We found that injury patterns between sledding and un-helmeted bicycling are similar," he adds. "While helmet use is widely accepted to prevent head injuries to bike riders, recommendations for sledding still lag far behind."
Bailey's recovery
Nine years ago, a Mott team led by craniofacial plastic surgeon Steven Kasten, M.D., and neurosurgeon Hugh Garton, M.D., started in the afternoon and worked through the night to address Bailey's complex facial injuries, carefully removing the bone from her forehead and using some of it to reconstruct her nose.
"This was probably the worst facial injury I've ever seen from a sledding accident," Kasten says. "Thankfully, there were no neurological injuries that would affect her brain function."
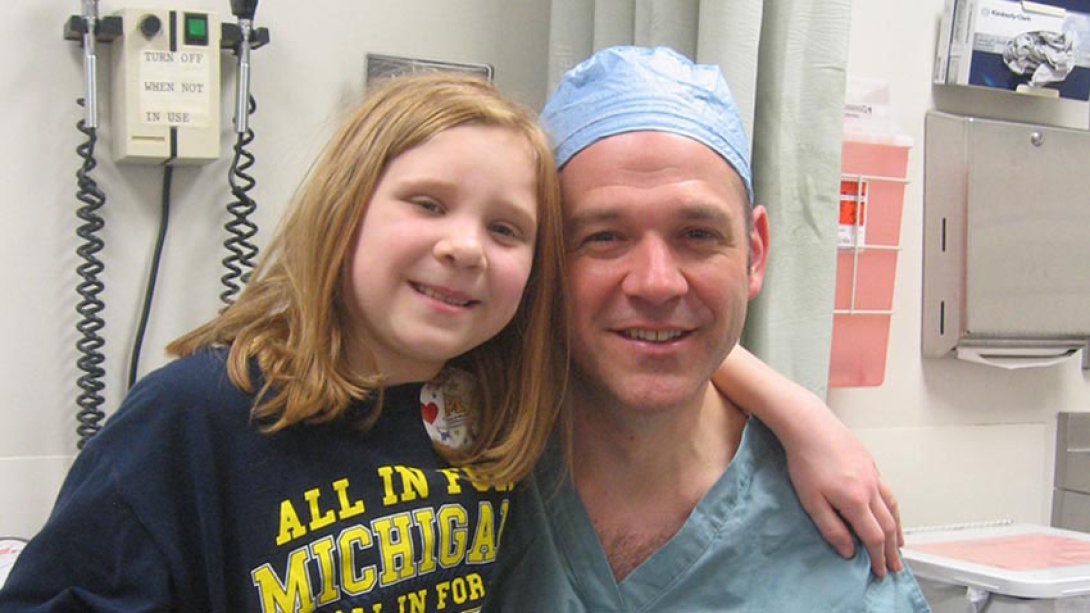
Today, there are few physical signs of the accident. But Bailey continued to need facial reconstruction surgeries at Mott and has struggled with breathing and sleeping.
Graves says Bailey avoided mirrors for a long stretch, and it took time to recover from the shock of the accident itself.
She isn't able to play contact sports but enjoys bowling, reading and time with her family.
We found that injury patterns between sledding and un-helmeted bicycling are similar. While helmet use is widely accepted to prevent head injuries to bike riders, recommendations for sledding still lag far behind.Peter Ehrlich, M.D.
Although the accident was traumatic, with long-term consequences, Graves says she knows Bailey was fortunate to escape brain injury or worse.
"It took more than 19 hours to put her back together. She's lucky not only to survive the accident, but also that kind of intense, long surgery, even though she was in the best hands," Graves says. "We just feel so blessed. We want to help others not go through what we did."
Sledding safety tips
Experts from the Pediatric Trauma Injury Prevention program at Mott offer some suggestions to keep kids safe while sledding this season:
-
Thoroughly check your surroundings to make sure the hill is free of collision risks, such as light posts, trees or rocks.
-
Avoid hillsides that end near streets, parking lots, ponds, fences or other hazards.
-
Children should never ride a sled that is being pulled by a motorized vehicle, including all-terrain vehicles, snowmobiles, tractors and dirt bikes.
-
Choose hills that are snowy rather than icy.
-
Sled during the daytime or in well-lit areas at night so hazards are visible.
-
Children should wear a fitted winter sport helmet designed for activities like skiing — or at least wear a bike helmet. Remember, sledding is often just as fast as or faster than riding a bike. Make sure heads are protected.
-
Kids shouldn't race each other or lie on top of each other or parents while sledding.
-
Avoid scarves, loose accessories or clothing that could get caught in a sled and pose risks.

Explore a variety of healthcare news & stories by visiting the Health Lab home page for more articles.

Department of Communication at Michigan Medicine
Want top health & research news weekly? Sign up for Health Lab’s newsletters today!