A quick and painless test designed to detect heart problems has benefits and shortcomings. And deciding who should get it also remains a subject of debate.
1:00 PM
Author |
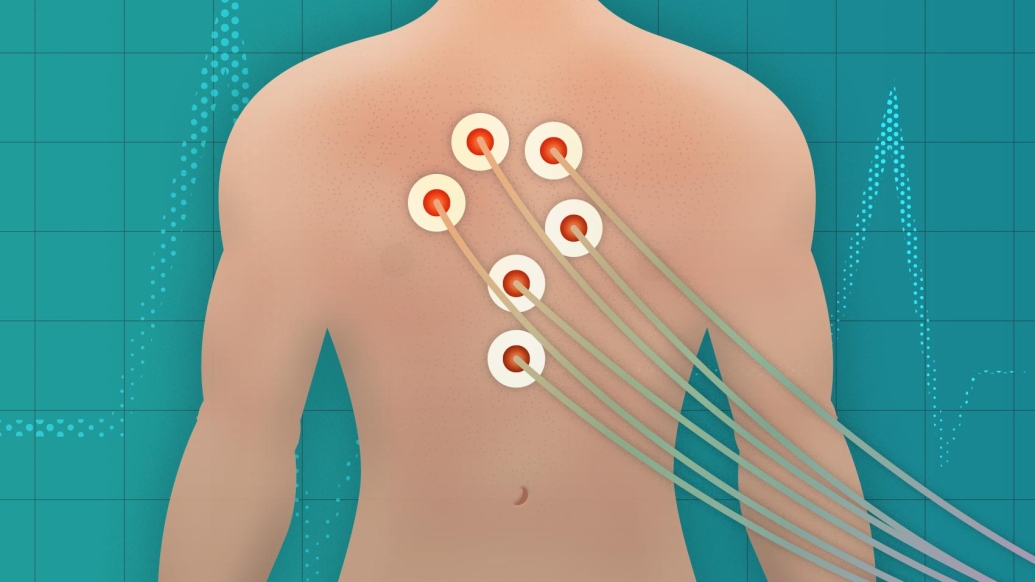
An electrocardiogram (EKG) monitors the heart's electrical activity. Using electrodes attached to the skin, it can help determine if a person has undiagnosed — and potentially fatal — cardiac problems.
MORE FROM MICHIGAN: Sign up for our weekly newsletter
Groups offering the test to teens have grown in recent years. A key target: students who might be at risk while playing sports. About 1 in 80,000 high school athletes dies each year from sudden cardiac arrest.
A timeout should come first, one expert says.
The intent of such screenings is valid, but the results can be imperfect or even misleading, says David Bradley, M.D., a pediatric electrophysiologist at University of Michigan C.S. Mott Children's Hospital.
"EKGs are a really great tool and provide a lot of information about the heart, but how exactly to use them to screen large populations of students is the part that's debatable," says Bradley, who notes that some screening bodies are for-profit entities.
"Even with the best intentions, these programs can fall short."
Growing consensus
The American Heart Association and the American College of Cardiology both agree. They issued a statement in 2014 recommending against mass EKG screenings in young people. And the NCAA last year released EKG screening guidelines that stopped short of requiring college athletes to get one.
The reason: EKGs return false-positive results between 5 and 20 percent of the time, Bradley says, which could "limit a person from an activity they like" without cause. And the tests miss serious issues in about 5 percent of cases, he adds.
"Parents may feel after a community EKG screening event that their child is in the clear and that everything has been ruled out," Bradley says. "Unfortunately, a large portion of the deaths we see from sudden cardiac arrest in youth are from abnormalities not detected by EKG."
Among the issues an EKG may detect:
-
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, an inherited condition in which the heart's walls are excessively thick, making it difficult for the heart to pump blood. Many people show no symptoms — and it is the leading cause of death among young athletes.
-
Coronary artery abnormalities that can reduce the flow of oxygen to the heart. Such congenital anomalies are the second-leading cause of sudden cardiac death in young athletes.
-
Long QT syndrome, a heart rhythm disorder marked by fast or chaotic heartbeats. It is a genetic disease most commonly triggered by physical exertion or emotional stress.
A need for conversation
No young life should be lost because of an undiagnosed cardiac condition, Bradley says.
While EKGs play a useful and important role, they should be part of a comprehensive review of a patient's health — not a starting point — and given only if deemed necessary, he says.
That review can begin with a visit to a primary care physician. An annual school or sports-related physical exam should include a detailed review surveying a teen and his or her parents about the family's history of heart disease and conditions.
SEE ALSO: What You Should Know About Counseling and Testing for Genetic Heart Disease
"Trust your primary care provider," says Bradley. "They are very sensitive to this issue. They know the alarming aspects of family history and background that would prompt a (cardiologist) referral."
The exchange shouldn't be limited to young athletes. The American Heart Association recommends all children receive such an evaluation.
Parents, meanwhile, must bring up any health concerns witnessed in their child. These may include chest pain, fainting, unexplained fatigue, high blood pressure and presence of a heart murmur.
Then, if circumstances dictate, a doctor can help recommend what steps — an EKG or otherwise — should follow.
Detection of a heart problem doesn't always mean sports are off the table.
Says Bradley: "It's a rather broad palette of possibilities. Some children will never be able to play competitively again. Others can pick up exactly where they left off."

Explore a variety of healthcare news & stories by visiting the Health Lab home page for more articles.

Department of Communication at Michigan Medicine
Want top health & research news weekly? Sign up for Health Lab’s newsletters today!