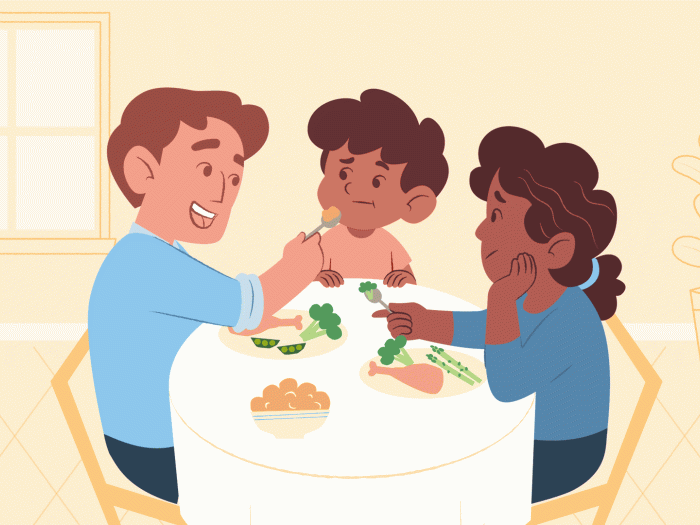
A survery suggests actively supporting time spent outside could help promote overall well-being among teens and young adults.
10:14 AM
Author |

Taking a walk in the park or just going outdoors could help youth feel better, and promoting public health policies that actively support time spent outside could help promote overall well-being among teens and young adults, according to a new University of Michigan survey.
"Our findings suggest that spending time in nature,-which youth define broadly as being outside, being around trees and woods and greenery, can have strong public health implications, given that youth might not need to travel as far or spend a lot of money to access nature," said Astrid Zamora, a fourth-year doctoral student at University of Michigan's School of Public Health and lead researcher of the report published on BMC Public Health.
"We know that mental health issues are highly prevalent among Americans in general, and we also know that it's very costly to access and utilize mental health services."
MORE FROM MICHIGAN: Sign up for our weekly newsletter
For their study, researchers used MyVoice, a text messaging poll designed to gather fast and qualitative responses from youth ages 14-24. In September 2020, researchers sent five open-ended questions that aimed to assess perceptions regarding nature to 1,174 participants. Qualitative responses were later analyzed.
They found that of the 994 respondents, many felt that spending time in nature positively impacted their mental health:
-
52% mentioned that it made them "feel calm when I am out in nature," 22% said that it relieved stress or "reduces my anxiety" and 17% felt that being in nature positively impacted their physical health and "makes me feel more active and in shape."
-
88% want to spend more time in nature, with 22% mentioning barriers impeding them from doing so.
Zamora said mental and physical health of youth has been a growing public health concern in the United States, yet many youth continue to lack access to services.
"We know that youth experience a variety of physiological, lifestyle and behavioral changes during this life stage, which may place them at an increased risk of experiencing both poor mental and physical health," she said. "What we also know is that today's youth are spending a lot less time in nature than previous generations with the uptake of technology likely being one of many factors associated with this decline.
"We feel this information would be imperative in informing community-level policies and interventions that aim to support youth mental and physical health."
MyVoice is directed by Tammy Chang, M.D., M.P.H., M.S., associate professor of family medicine at Michigan Medicine and a member of the U-M Institute for Healthcare Policy and Innovation.
This article was originally posted on the Michigan News website.
Like Podcasts? Add the Michigan Medicine News Break on iTunes, Google Podcasts or anywhere you listen to podcasts.

Explore a variety of healthcare news & stories by visiting the Health Lab home page for more articles.

Department of Communication at Michigan Medicine
Want top health & research news weekly? Sign up for Health Lab’s newsletters today!